Data Integration Centre Essen
As one of the German Medical Informatics Initiative’s (MII) data integration centres (DIC), the DIC Essen was established in recent years to enable the collection, integration, and exchange of medical data in such a way that it can be used effectively in clinical care and research. The tasks of the DIC Essen include the import of data from a wide range of clinical subsystems in the university hospital as well as the integration and processing of this data while ensuring data quality and data protection. The processed data is made available for use in research and research results are fed back into clinical care via the DIC.
The DIC Essen provides various services to three types of users: clinicians, internal and external researchers, and patients. This is facilitated by its structure: the DIC is separated into a Clinical Domain and a Research Domain. The Clinical Domain contains non-pseudonymized data and serves the development of clinical applications, while the research domain contains pseudonymized data for research purposes.
The DIC Essen was not developed from scratch but builds on substantial previous work: The DIC operates on top of SHIP, the Smart Hospital Information Platform. Originating in the Institute of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology, SHIP has been developed for more than 10 years and has enabled the UME to significantly shape the concept of the Smart Hospital in Germany and to play a pioneering role in its implementation. SHIP is a native citizen of the FHIR ecosystem. It supports the transfer of medical data from various clinical subsystems into the FHIR format. During the transformation process, data is enriched with semantic codings such as SNOMED CT, LOINC, ICD and ATC to ensure interoperability and compliance with MII core data set specifications and standard terminologies.
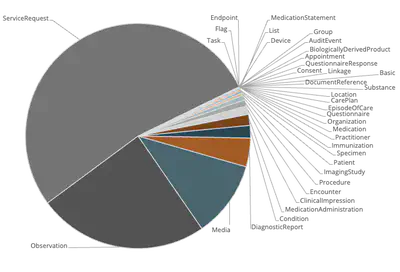
By integrating SHIP into the DIC, the data storage in the Clinical Domain contains already more than one billion FHIR resources with data of more than one million patients. All this data is accessible for local applications in the Clinical Domain to support clinicians. Beyond that, SHIP serves also as the foundation for developing various applications in cooperation with industrial partners to increase patient involvement and provide services for patients.
Due to SHIP, the DIC Essen is one of the most productive data integration centres in Germany with more than one billion FHIR resources in the Clinical Domain. The DIC was established in cooperation with the Institute for Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (IKIM) and UME’s Central IT department (ZIT). Organizationally, it is integrated into the latter.
- diz(at)uk-essen.de
- Institute for AI in Medicine, Girardetstraße 2, 45131, Essen, Germany

